
Case #4
-
History: Left flank pain and nausea. Evaluate for kidney stones. No hematuria.
© 2012 Must See Radiology

History: Left flank pain and nausea. Evaluate for kidney stones. No hematuria.
© 2012 Must See Radiology
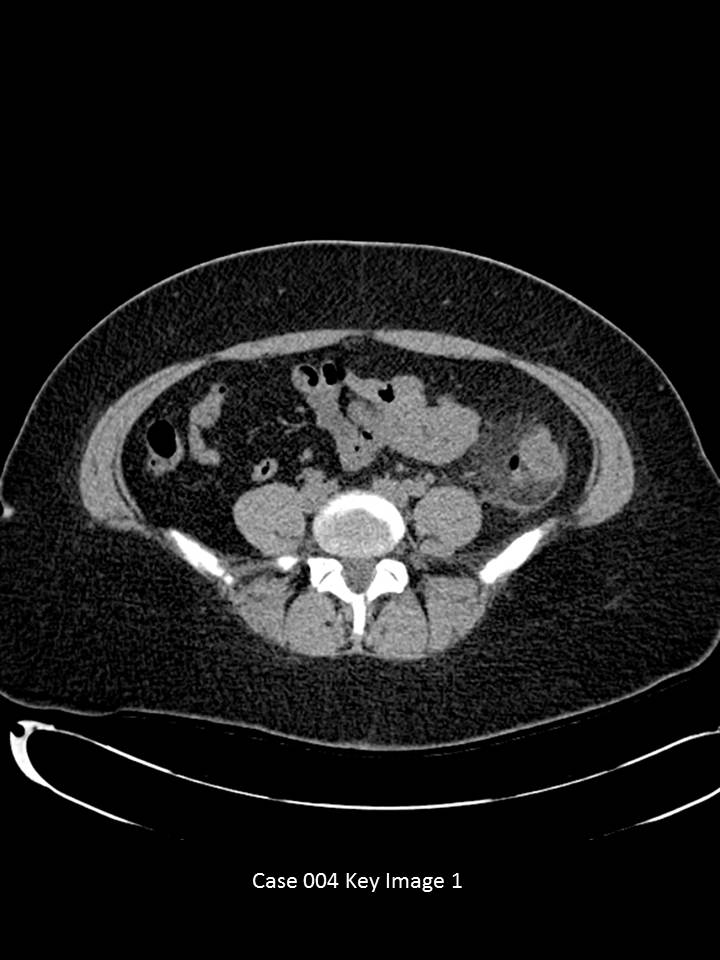
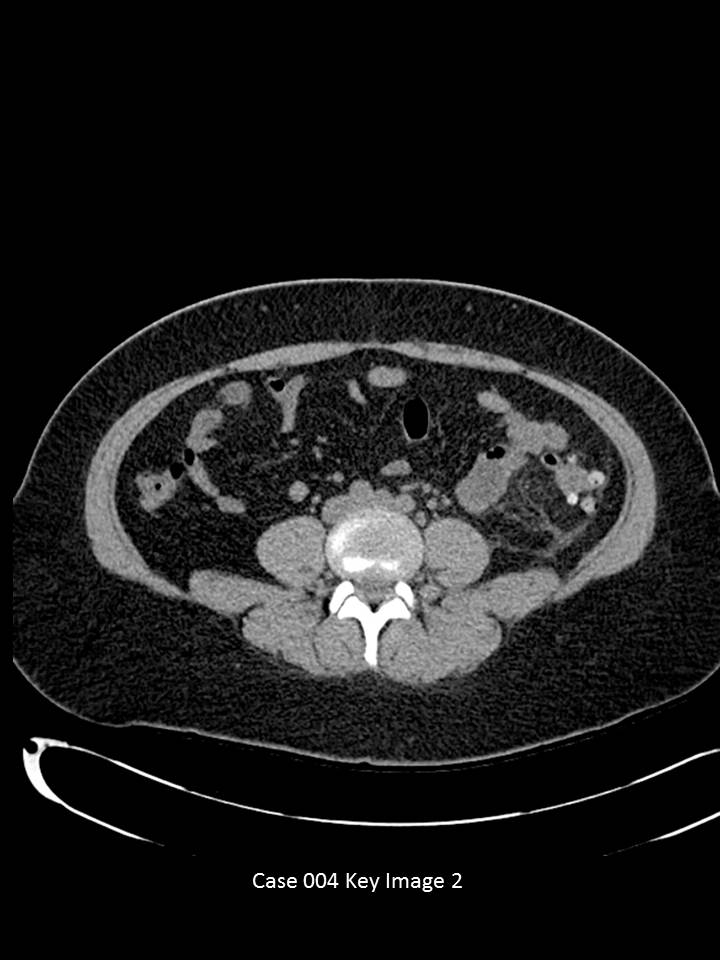
Axial CT images of the abdomen and pelvis through the mid-abdomen with no IV or oral contrast.
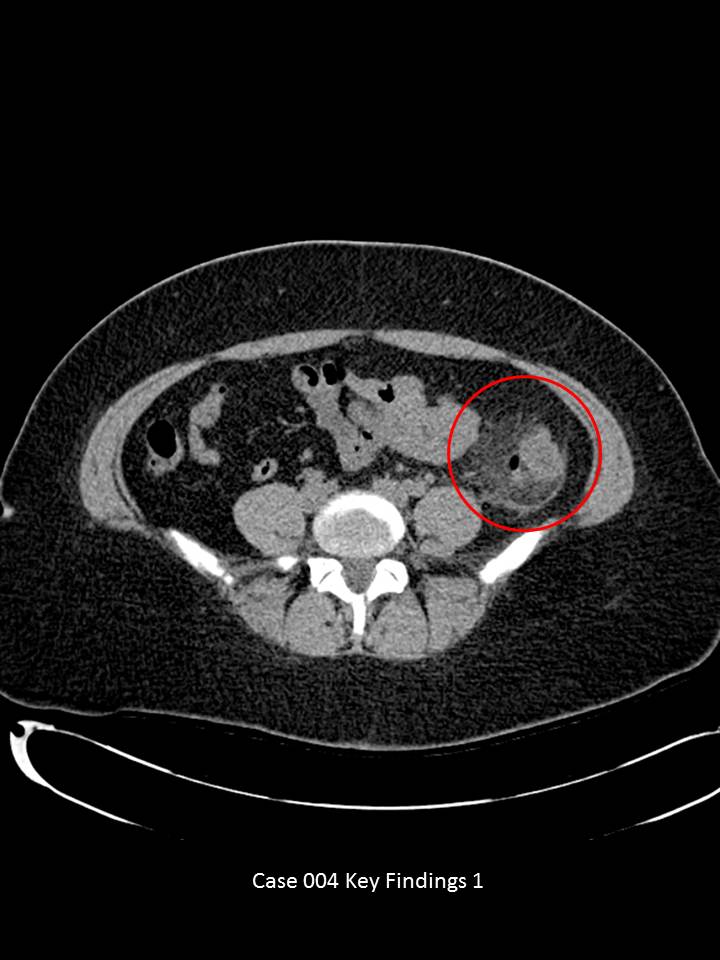
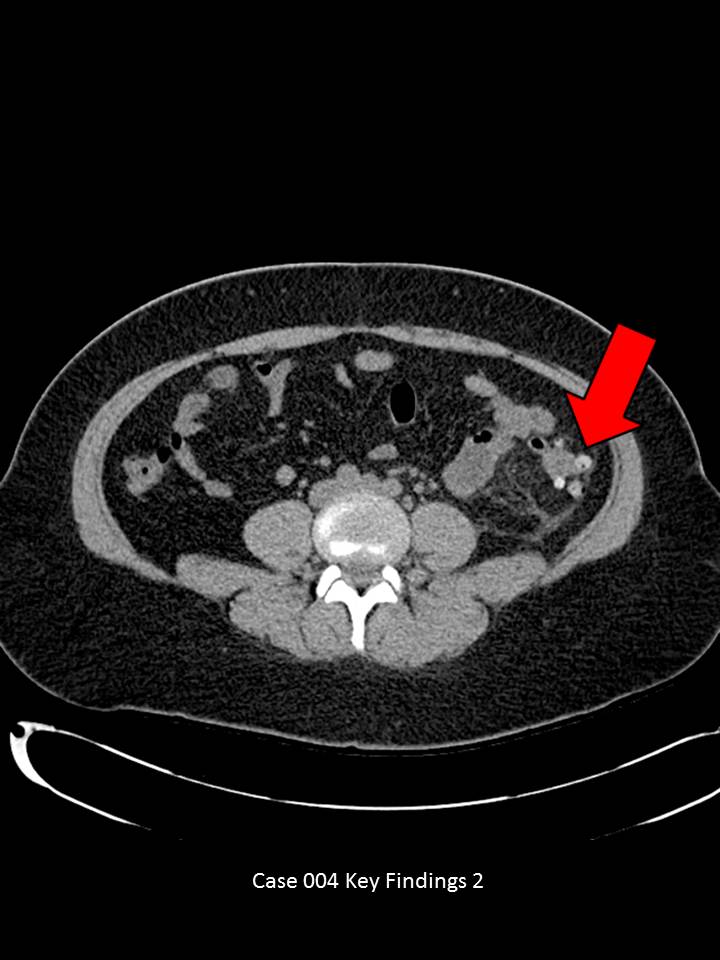
Axial images through the lower abdomen demonstrate multiple colonic diverticula. Some appear hyperdense (red arrow) and others with air. There is significant pericolonic fat stranding and peritoneal thickening (red circle). No significant free intraperitoneal air or fluid. No abscess or fistula formation. No obstructive urolithiasis.
© 2012 Must See Radiology
Acute Diverticulitis (mild)
This patient presented with vague left flank pain symptoms. The CT exam demonstrates acute diverticulitis (colonic diverticula, peripheral fat stranding, thickened peritoneum). The patient was treated medically because no surgical complications of diverticulitis were present.
When diverticulitis is identified, always evaluate for abcess, fistula (bladder/vaginal/small bowel), obstruction or free intraperitoneal air. ER physicians should be aware if these findings are present to determine whether the patient requires surgical consultation. Also, direct visualization with colonoscopy in patients over the age of 50 and after the patient is recovered from the acute inflammation is recommended to evaluate for any underlying colon malignancy.
Complications of Diverticulitis:
Additional Information:
Horton KM. "CT Evaluation of the Colon: Inflammatory Disease." March 2000 Radiographics: 20, 399-418.
© 2012 Must See Radiology
Not available at this time.
Rating not available at this time.
Any feedback regarding this case can be emailed to Tony@mustseeradiology.com
Thank you for trying Must See Radiology!
© 2012 Must See Radiology