
Case #7
-
History: 20-year-old female with abnormal menses, lower pelvic pain, urine pregnancy test +, beta-HCG is pending.
© 2012 Must See Radiology

History: 20-year-old female with abnormal menses, lower pelvic pain, urine pregnancy test +, beta-HCG is pending.
© 2012 Must See Radiology
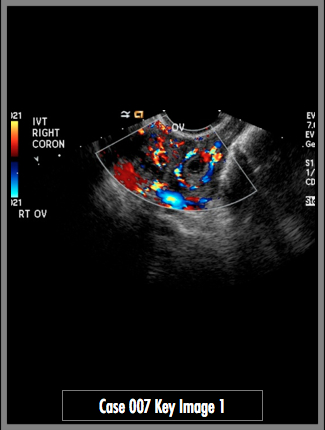

Pelvic Ultrasound, transvaginal technique with color Doppler, viewing the right ovary and uterus.
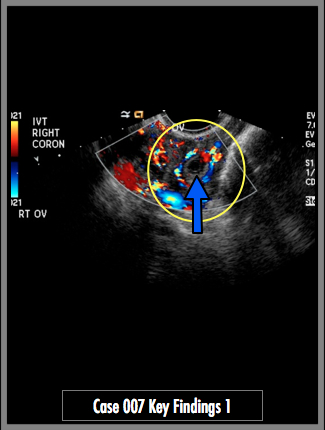

Transvaginal images of the right adnexa demonstrate a complex cystic lesion with internal septations. Color Doppler images demonstrate abnormal increased flow around the cystic structure in the right adnexa (ring-of-fire sign). Finding in the right adnexa represents a gestational sac. No intrauterine pregnancy is identified (yellow arrow).

## ADDL IMAGES ##
© 2012 Must See Radiology
Ectopic Pregnancy, Right Adnexa
Ectopic Pregnancy can be expected in pregnant women >6 weeks gestational age, with + B-hCG (>1000) and no intrauterine signs of pregnancy. An echogenic mass (embryo) in the adnexa is commonly seen. An embryo with a heartbeat in the adnexa is pathognomonic for ectopic pregnancy. Be advised, up to 35% of ectopic pregnancies have normal appearing adnexal structures.
Locations for ectopic pregnancy include the fallopian tubes (95%), cervix (<1%), ovaries (3%), abdomen(<1%).
Ectopic pregnancy may occur alongside an intrauterine pregnancy (heterotopic pregnancy). This condition may become more likely as more women are undergoing ovulation induction.
If the diagonsis is unclear, repeat US and serial B-hCG testing may be helpful. B-hCG levels rise slower in ectopic pregnancies than uterine pregnancies, i.e. less than 50% rise in serial B-hCG levels at 48-hour intervals.
Additional Information:
Lin, EP. "Diagnostic Clues to Ectopic Pregnancy." October 2008 RadioGraphics: 28, 1661-1671.
© 2012 Must See Radiology
Not available at this time.
Rating not available at this time.
Any feedback regarding this case can be emailed to Tony@mustseeradiology.com
Thank you for trying Must See Radiology!
© 2012 Must See Radiology