
Case #6
-
History: Sharp left flank pain for 2 days with nausea & vomiting
© 2012 Must See Radiology

History: Sharp left flank pain for 2 days with nausea & vomiting
© 2012 Must See Radiology
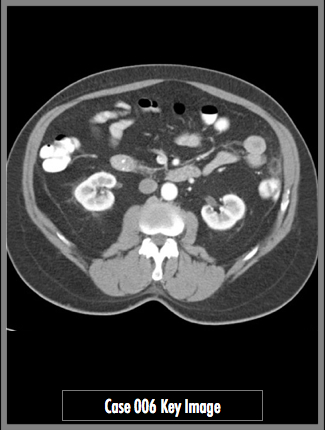
Axial CT Abdomen and Pelvis with IV and oral contrast through the level of the kidneys
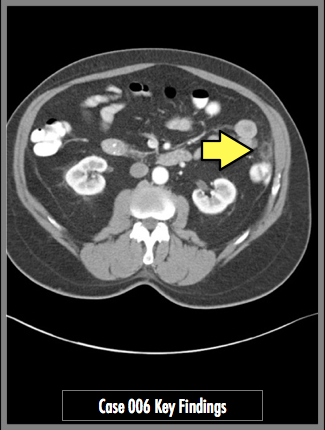
Axial images through the lower abdomen demonstrate a round area of pericolonic fat stranding with central fat attenuation and a peripheral hyperattenuating rim. No colonic wall thickening. No colonic diverticular disease.
© 2012 Must See Radiology
Epiploic Appendagitis
Epiploic Appendagitis presents as acute abdominal pain that is focal. It can mimic symptoms of appendicitis, cholecystitis or diverticulitis. This is not a surgical emergency and can be treated medically. It is important to know because making the correct diagnosis and communicating with the surgeon can prevent an unnecessary surgical operation. Characteristic CT findings are listed in the Key Findings portion of this case.
The epiploic appendage is a peritoneal pouch, attached to colon by a vascular stalk. When they twist, the vein portion of the stalk can be occluded, leading to ischemia and inflammation. Clinical clues to the diagnosis can include obesity, unaccustomed exercise, and hernia.
Prognosis: usually resolves clinically in 2 weeks (CT findings may take up to 6 months to clear). Treatment is usually with anti-inflammatory medicines only. Antibiotics and surgical operations are used in rare occasions only.
Additional Information:
Singh, AK. "Acute Epiploic Appendagitis and Its Mimics." November 2005 Radiographics: 25, 1521-1534.
© 2012 Must See Radiology
Not available at this time.
Rating not available at this time.
Any feedback regarding this case can be emailed to Tony@mustseeradiology.com
Thank you for trying Must See Radiology!
© 2012 Must See Radiology